How AI Enhances Traditional Knowledge Bases: A Deep Dive

Table of contents
Knowledge bases are like big online help centers. Companies use them to put answers to common questions in a centralized place. This way, customers can quickly find what they need without waiting for help. It’s a win-win: customers get fast answers, and support teams can spend more time on more critical tasks.
But as technology has grown, there’s been a push to make these knowledge bases even more helpful. That’s where AI, or Artificial Intelligence, comes in.
By leveraging AI, knowledge bases can work faster and understand questions better. It’s like giving them a small upgrade to be more efficient.
Companies see the value in this. With AI, they can provide answers more quickly and make sure customers find what they need. In this article, we’ll discuss why this change is happening and what it means for both companies and customers.
Table of Contents
- What is a Knowledge Base?
- What is an AI Knowledge Base?
- Key Components of an AI Knowledge Base
- Benefits of AI Knowledge Base for Customer Support
- Difference Between AI Knowledge Base and Traditional Knowledge Base
- Steps to Build an AI Knowledge Base for Customer Service
- 6 Best AI Knowledge Base Tools
- Empower Customers to Self-Serve
What is a Knowledge Base?
A Knowledge Base, in the context of customer service or customer support, refers to a centralized repository of information that provides answers to frequently asked questions, solutions to common problems, and detailed guidance on product or service-related topics.
It is designed to empower both support agents and customers with quick access to the necessary information, reducing the need for direct interactions for common queries.
What is an AI Knowledge Base?
An AI Knowledge Base, in the context of customer support, refers to an advanced, centralized repository of information that is not only structured for human comprehension but is also optimized for machine understanding. It leverages artificial intelligence to automatically update its content, draw inferences, and provide more contextually relevant and personalized responses to user queries.
Imagine a customer named Jane who recently purchased a smart thermostat from a company. She’s having trouble with the installation process. Instead of reaching out to customer support directly, she interacts with the company’s AI-powered chatbot. Jane types, “I can’t connect my thermostat to Wi-Fi.”
The chatbot, integrated with the AI Knowledge Base, understands the context (Jane is a recent purchaser, and her issue is with Wi-Fi connectivity) and provides a step-by-step solution tailored to her product model, along with a video tutorial. The AI Knowledge Base has learned from previous similar queries and offers the most effective solution, ensuring a smooth experience for Jane.
Key Components of an AI Knowledge Base
Here are the key components of an AI Knowledge Base, along with relevant examples:
- Articles and FAQs: These are detailed answers to commonly asked questions. They serve as the primary source of information for many AI-driven customer support systems. For instance, a customer might ask, “How do I reset my password?” The KB would have an article detailing the steps to reset the password.
- Structured Data: This refers to organized information that the AI can quickly access and use to provide specific answers. Let’s say a customer might ask about the warranty period for a product. The AI can pull this specific data from the knowledge base.
- Decision Trees: These are flowcharts or diagrams that guide the AI in troubleshooting or problem-solving by following a logical sequence of steps. For example, if a customer reports an issue with a device not turning on, the decision tree might guide the AI to first ask if the device is charged, then if the power button is working, and so on.
- User Feedback Loop: This allows the AI to learn from user interactions. If a user indicates that an answer was not helpful, the AI can use this feedback to improve future responses. For instance, after providing a solution, the AI might ask, “Was this answer helpful?” Based on the response, the KB can be updated or refined.
- Metadata and Tags: These help categorize and quickly retrieve relevant information from the KB. They can be used to filter and present the most appropriate answers to user queries. Example: A query about “billing” might pull up articles tagged with “billing,” “invoices,” or “payments.”
- Multimedia Content: In addition to text, a modern AI-powered knowledge base might include images, videos, and other multimedia to assist in explaining solutions. Let’s say, for a customer query about assembling a product, the KB might provide a step-by-step video tutorial.
- Integration Points: These allow the AI to pull in real-time data or connect with other systems to provide more personalized support. Example: If a customer asks about the status of their order, the AI might integrate with the order management system to provide a real-time update.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Modules: These enable the AI to understand and interpret human language, making the interaction more intuitive and efficient. For example, a customer might phrase a question in many ways, like ‘How do I set up my account?’ or ‘Help me with account setup.’ NLP ensures the AI understands the intent behind different phrasings. Graph-based RAG models further enhance this capability by improving response accuracy through structured data retrieval.
Benefits of AI Knowledge Base for Customer Support
Implementing an AI Knowledge Base in customer support can offer a multitude of advantages, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Here are some of the prominent benefits explained in detail:
1. 24/7 Availability:
AI Knowledge Bases can operate around the clock, ensuring that customers can find answers to their queries at any time of the day or night. This 24/7 availability is particularly beneficial for businesses with a global customer base, accommodating different time zones seamlessly.
2. Cost-Efficiency
By automating routine queries, businesses can allocate human resources to more complex and nuanced tasks, optimizing operational costs. AI Knowledge Bases can handle a large volume of queries simultaneously, allowing businesses to scale their customer support.
3. Personalized Service
AI systems can analyze customer data to provide personalized responses, enhancing the customer experience. Over time, AI can learn from customer interactions to continually refine and personalize the service it offers.
4. Data-Driven Insights
AI Knowledge Bases can analyze customer queries to provide insights into common issues, preferences, and trends. This helps businesses anticipate customer needs and proactively address them.
5. Multilingual Support
AI Knowledge Bases can offer support in multiple languages, breaking down language barriers and expanding the business’s reach. AI can be trained to understand and respond to cultural nuances, offering a more inclusive customer service experience.
6. Improved Accuracy and Consistency
AI systems can provide accurate and consistent responses to customer queries, reducing the likelihood of errors that can occur with human agents. AI ensures that customers receive standardized responses, maintaining a consistent brand voice.
7. Integration with Other Systems
AI Knowledge Bases can be integrated with other business systems, such as CRM and ERP, to provide a unified platform for customer support. In cases where human intervention is required, AI can facilitate a seamless transition from the automated system to a human agent.
8. Self-Service Options
AI Knowledge Bases empower customers to find answers to their queries through self-service options, reducing dependence on customer support agents. AI can offer interactive tools, such as chatbots, to guide customers in finding the information they need.
9. Enhanced Security
AI systems can be designed with robust security features to protect customer data and ensure privacy. AI can also assist in detecting and preventing fraud by analyzing patterns and identifying suspicious activities. These AI systems are great at protecting against identity theft, constantly watching for any unauthorized access, and quickly letting you know if something’s up.
Using Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) alongside can also significantly bolster your overall security framework. DSPM helps identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities in your data infrastructure, making sure that the sensitive information handled by your AI system remains protected. It can provide an additional layer of security, particularly important when dealing with large volumes of customer data in AI-driven support systems.
10 Best Knowledge Base Software for Your Business [2025]
Difference Between AI Knowledge Base and Traditional Knowledge Base
1. Nature of Information Retrieval
AI Knowledge Base:
Dynamic Information Retrieval: AI Knowledge Bases are designed to understand and interpret user queries, even if they are not phrased in the exact same way that the information is stored. This is achieved through natural language processing (NLP) capabilities. The AI can understand the context, sentiment, and intent behind a query, allowing for more flexible and intuitive search results.
Example: If a user types “How do I reset my password?” into an AI-driven support knowledge base, the system might return results related to password reset procedures, even if the exact phrasing isn’t present in any knowledge base article. It understands the user’s intent and provides the most relevant information.
Traditional Knowledge Base:
Static Information Retrieval: Traditional knowledge bases rely on exact keyword matching or predefined taxonomies. If a user’s query doesn’t match the stored keywords or phrases, the system might not return relevant results.
Example: In a traditional support knowledge base, if a user types “How do I change my passcode?”, but the stored article uses the term “password” instead of “passcode”, the system might not return the relevant article, even though the user’s intent is clear.
2. Learning and Adaptation
AI Knowledge Base:
Continuous Learning: One of the defining features of an AI Knowledge Base is its ability to learn and adapt over time. As users interact with the knowledge base, the AI system can analyze search patterns, frequently asked questions, and user feedback to refine its responses.
Example: Suppose a new product feature is launched, and users start asking questions about it in the AI Knowledge Base. Even if there isn’t a dedicated article about this feature initially, the AI can recognize the surge in similar queries and prioritize creating or suggesting content related to that topic. Additionally, if users consistently mark a certain answer as unhelpful, the AI can adjust its future responses accordingly.
Traditional Knowledge Base:
Static Content: Traditional knowledge bases don’t have the capability to learn or adapt on their own. Content updates, refinements, and improvements are manual processes that require human intervention. This means that if there’s a gap in the knowledge base or if certain content becomes outdated, it won’t be addressed until someone manually updates it.
Example: If users are consistently searching for a topic that isn’t covered in a traditional knowledge base, there’s no system in place to recognize this gap. It would rely on human administrators to notice the trend, and then take action to create or update the relevant content.
3. Personalization and User Experience
AI Knowledge Base:
Personalized Responses: AI Knowledge Bases can provide personalized responses based on user behavior, preferences, and past interactions. By analyzing a user’s history and profile, the AI can tailor its responses to better suit individual needs, making the experience more relevant and efficient.
Example: Consider a software platform that has both beginner and advanced users. When a beginner asks, “How do I start a new project?”, the AI Knowledge Base might provide a step-by-step guide with basic instructions. However, for an advanced user with a history of using complex features, the same query might yield a more detailed response, perhaps highlighting advanced settings or shortcuts.
Traditional Knowledge Base:
One-Size-Fits-All: Traditional knowledge bases provide the same information regardless of who’s asking. They lack the capability to differentiate between users or to tailor responses based on individual needs. Every user, whether a novice or an expert, receives the same set of answers.
Example: Using the same scenario of a software platform, if both beginner and advanced users ask the traditional knowledge base, “How do I start a new project?”, they would receive the exact same article or set of instructions, without any consideration for their differing skill levels or needs.
4. Integration and Interactivity
AI Knowledge Base:
Interactive Features: AI Knowledge Bases often come equipped with interactive features like chatbots, voice assistants, or recommendation systems. These features allow users to engage in a more conversational manner, ask follow-up questions, and receive real-time feedback. The AI can also proactively suggest related articles or topics based on the user’s current query.
Example: A user visiting an online store’s help center might initially ask, “How do I return a product?”. After receiving the return procedure, the AI Knowledge Base might proactively suggest, “Would you also like to know about our refund policy?” This anticipatory guidance enhances user experience and provides comprehensive support.
Traditional Knowledge Base:
Static Interaction: Traditional knowledge bases typically present information in a static format, such as articles, FAQs, or PDFs. Users need to navigate through categories or use search functions to find what they’re looking for. There’s limited scope for real-time interaction, and users don’t receive proactive suggestions based on their queries.
Example: In the same online store scenario, a user searching for return procedures in a traditional knowledge base would find the relevant article, and that’s it. They would need to initiate a new search to find out about the refund policy, without any prompts or suggestions from the system.
5. Maintenance and Content Update
AI Knowledge Base:
Automated Content Suggestions: AI Knowledge Bases can automatically suggest content updates based on user interactions and emerging trends. By analyzing search patterns, user feedback, and content gaps, the AI can highlight areas that need new articles, updates, or revisions. This proactive approach ensures that the knowledge base remains up-to-date and relevant without constant manual oversight.
Example: If a software company releases a new update and users start asking questions about a specific new feature, the AI Knowledge Base can identify this trend and suggest the creation of a new article or tutorial about that feature. Additionally, if a particular article is receiving negative feedback or is being bypassed by users, the AI can flag it for review or revision.
Traditional Knowledge Base:
Manual Oversight Required: The maintenance and updating of a traditional knowledge base are entirely manual processes. Administrators or content managers need to regularly review the content, track user feedback, and identify gaps or outdated information. This can be time-consuming, and there’s a higher risk of missing out on important updates.
Example: Following the software update scenario, in a traditional knowledge base, unless users directly reach out to support or there’s a dedicated team constantly monitoring user queries, the need for a new article about the updated feature might go unnoticed. Outdated articles might remain unchanged for long periods, leading to potential misinformation.
6. Scalability and Data Analysis
AI Knowledge Base:
Scalable Insights: AI Knowledge Bases are inherently designed to handle vast amounts of data and extract meaningful insights from them. As the volume of user interactions grows, the AI can efficiently analyze this data to identify patterns, preferences, and areas for improvement. This scalability ensures that even as the user base or content volume expands, the knowledge base remains efficient and effective.
Example: A global company with millions of users might receive diverse queries in multiple languages. An AI Knowledge Base can analyze these interactions to identify common questions across regions, detect emerging trends in real time, and even offer insights into potential product improvements based on user feedback.
Traditional Knowledge Base:
Limited Data Analysis: While traditional knowledge bases can store and present vast amounts of information, their capacity for data analysis is limited. Any insights or patterns would need to be manually extracted and analyzed, which can be cumbersome and less accurate, especially with large datasets. As the user base grows, it becomes increasingly challenging to glean actionable insights without advanced analytical tools.
Example: Using the same global company scenario, a traditional knowledge base might be able to store FAQs and articles in multiple languages, but identifying global trends or region-specific concerns would require manual data extraction and analysis, making it a time-consuming and potentially less accurate endeavour.
7. Multimodal Interaction and Accessibility
AI Knowledge Base:
Multimodal Engagement: AI Knowledge Bases can interact with users across multiple modes, be it text, voice, or even visual cues. With advancements in AI technologies like voice recognition and image processing, users can engage with the knowledge base in various ways, making it more accessible and user-friendly.
Example: A visually impaired user might prefer to interact with a knowledge base using voice commands. An AI Knowledge Base can understand and respond to these voice queries, providing answers audibly. Similarly, a user could upload a screenshot of an issue they’re facing, and the AI could analyze the image and provide relevant solutions.
Traditional Knowledge Base:
Text-Centric Interaction: Traditional knowledge bases are predominantly text-based. Users interact by reading articles, FAQs, or guides and typing in their queries. While some might offer multimedia content like videos or images, the primary mode of interaction is reading and typing, which might not be accessible or convenient for all users.
Example: A user with limited literacy skills or a disability might find it challenging to navigate and extract information from a text-heavy traditional knowledge base. They would need alternative resources or assistance to get the information they’re seeking.
Recommended read: 7 Tips for Making Your Video Knowledge Base User-Friendly
Steps to Build an AI Knowledge Base for Customer Service
Building an AI Knowledge Base for Customer Service involves a combination of data collection, machine learning, and integration with customer service platforms. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Define the Objective:
- Determine the specific problems you want the AI knowledge base to solve.
- Decide on the scope: Will it handle FAQs, technical issues, product details, or all of the above?
- Data Collection:
- Gather existing customer service data: This includes chat logs, emails, call transcripts, and other customer interactions.
- Collect FAQs, product manuals, and other relevant documentation.
- Ensure data privacy: Anonymize personal customer details and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
- Data Cleaning and Preprocessing:
- Remove redundant or irrelevant information.
- Standardize data formats.
- Segment data based on categories (e.g., billing, technical issues, product inquiries).
- Choose the Right AI Model:
- Depending on the complexity, you can start with rule-based systems or move to more advanced machine-learning models.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) models are particularly useful for understanding and generating human-like responses.
- Training the Model:
- Use the cleaned data to train your AI model.
- Regularly update the model with new data to improve accuracy.
- Validation and Testing:
- Test the AI system with a subset of your data to validate its accuracy.
- Conduct A/B testing to compare the AI’s performance against human agents or other systems.
- Integration:
- Integrate the AI knowledge base with your existing customer service platforms (e.g., chatbots, email systems, call centers).
- Ensure seamless handoff between the AI system and human agents for complex queries.
- User Interface Design:
- Design an intuitive interface for both customers and agents.
- Ensure the system provides clear and concise answers, with an option for users to request further clarification or speak to a human agent.
- Continuous Monitoring and Feedback Loop:
- Monitor the AI’s performance regularly.
- Collect feedback from customers and agents to identify areas of improvement.
- Use this feedback to refine and retrain the model.
6 Best AI Knowledge Base Tools
1. Hiver
Hiver is a Gmail-based customer support platform. In addition to helping support teams offer support via email, phone, WhatsApp, and chat, Hiver also helps them create a knowledge base. This ensures companies access shared knowledge and provide consistent responses to customer queries.
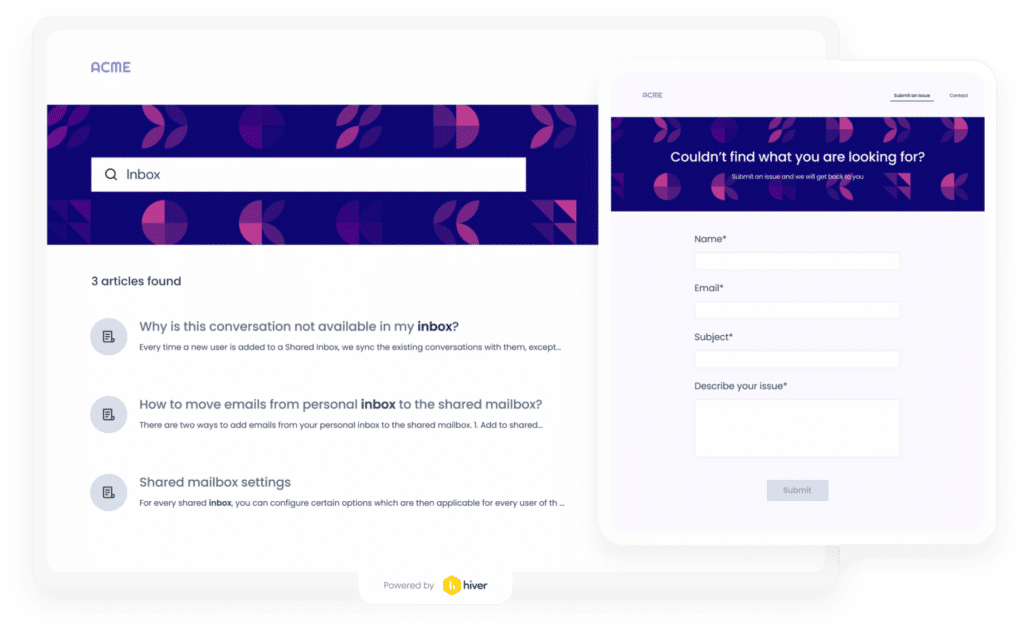
Key Features:
- Shared Knowledge Base: Hiver allows teams to create a centralized repository of canned responses and solution articles, ensuring that agents have quick access to consistent information.
- Easy Access within Gmail: Since Hiver operates within Gmail, agents can quickly pull information from the knowledge base without leaving their inbox, streamlining the response process.
- Feedback Mechanism: Agents can provide feedback on the relevance and effectiveness of knowledge base articles, helping to continuously refine and improve the content.
2. Document360
Document360 is an AI-powered knowledge base that offers an easy-to-use platform to create and publish a knowledge base for your customers or teams. Easily create and manage product documentation, SOPs, User manuals, Wikis, API documentation, and more. Use AI-powered search for accurate results in a fraction of a second and Eddy – AI Assistant for precise customer queries.
With Eddy, content creators can utilize AI writer features to develop outlines, recommend titles and tags, generate SEO meta descriptions, and save a lot of time in producing an article. It also offers a rich editor, comprehensive analytics, and seamless third-party integrations to streamline your documentation process effortlessly.
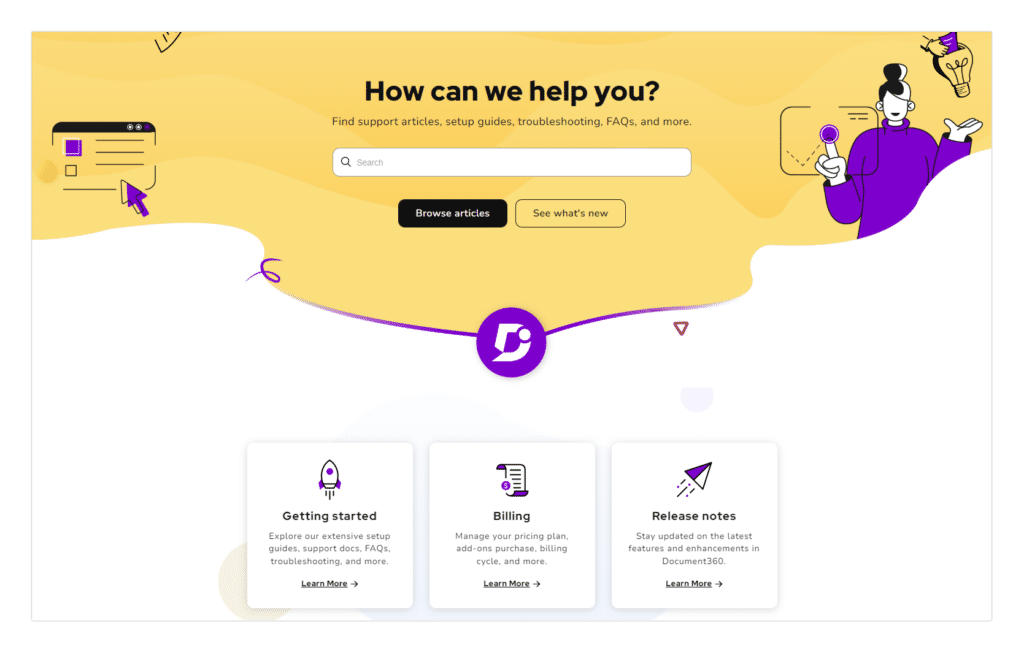
Key Features:
- Rich Editor: Draft articles using versatile editor options, including Markdown and advanced WYSIWYG editors for flexible content creation.
- Version Control: Access robust collaboration and version control features enabling simultaneous document editing by multiple users, easy forking of preferred versions, and seamless creation of new iterations.
- Category Manager: Organize and maintain structured documentation efficiently using categories and subcategories, enabling the clear organization and display of related content.
- Backup and Restore: Ensures data security with automatic daily backups and manual backup options, featuring restoration capabilities for Documentation, Home page builder, Custom CSS, and Custom JavaScript.
3. Zendesk Guide
Zendesk Guide is a leading knowledge base solution tailored for businesses aiming to empower both their customers and agents. By integrating AI capabilities, Zendesk Guide not only enhances user experience but also streamlines support operations.
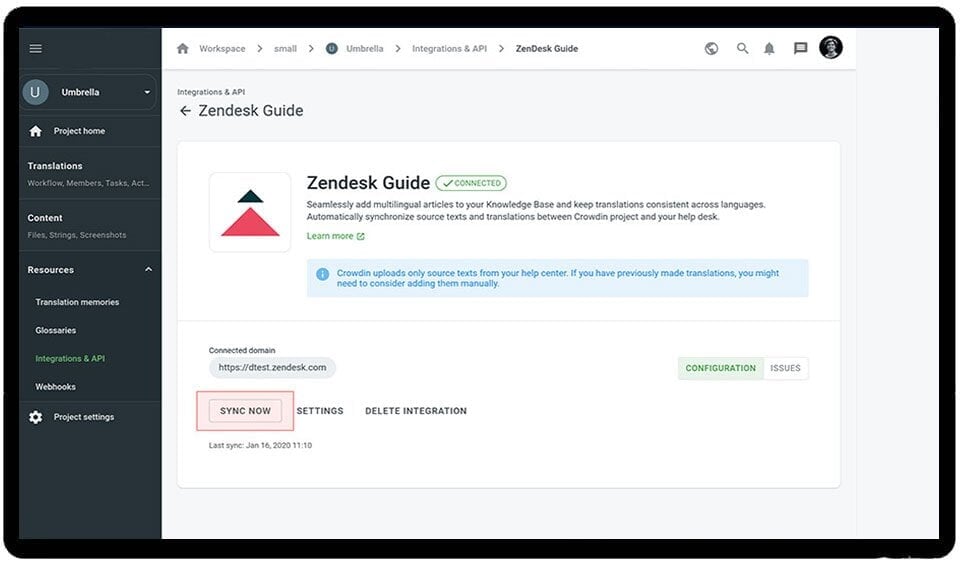
Key Features:
- Answer Bot: This AI-driven feature is designed to assist customers in real time. As users type in their queries, the Answer Bot automatically suggests relevant articles from the knowledge base. This not only provides instant solutions but also reduces the need for human agent intervention, leading to faster response times and increased efficiency.
- Content Cues: Leveraging AI analytics, Content Cues analyzes customer interactions and feedback to pinpoint gaps in the knowledge base. It suggests areas where new articles can be created or where existing ones need updates. This ensures that the content remains relevant and up-to-date, catering to the evolving needs of the customers.
- Machine Learning Search: Traditional search functionalities often rely on exact keyword matches, which can lead to irrelevant results. Zendesk Guide’s Machine Learning Search, however, continuously learns from user behavior. Over time, it improves the relevance of search results, ensuring that users find exactly what they’re looking for.
4. Kustomer
Kustomer is a customer service platform that emphasizes a holistic view of the customer, allowing support teams to deliver more personalized and efficient support. Its knowledge base capabilities are enhanced with AI to provide both agents and customers with the right information at the right time.
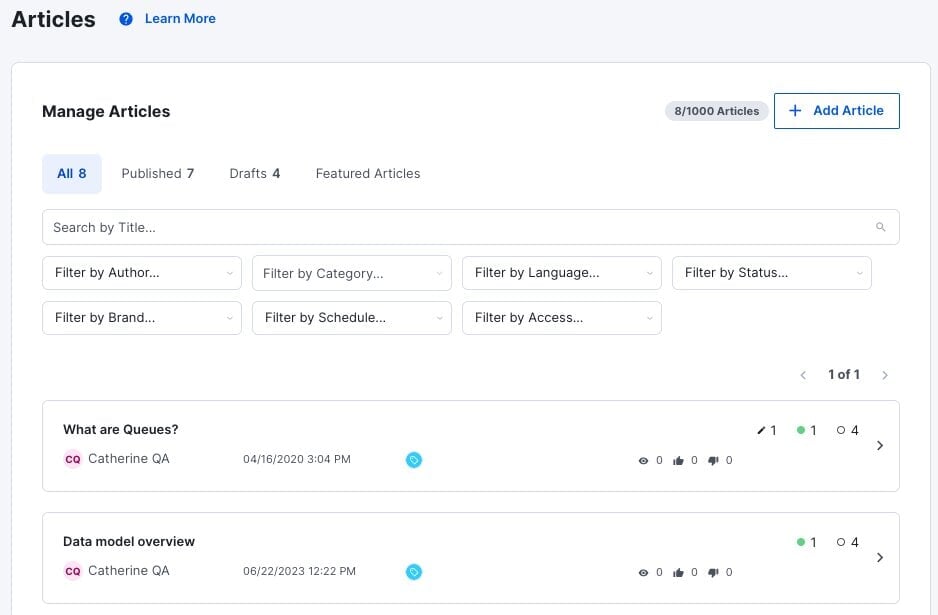
Key Features:
- Content Optimization: Kustomer’s AI analyzes which articles are most effective in resolving customer issues and suggests areas of improvement or new topics to the support team.
- Automated Responses: Based on the customer’s query, Kustomer can automatically suggest or send the most relevant knowledge base article, reducing the need for agent intervention.
- Feedback Loop: Customers can provide feedback on knowledge base articles, and the AI uses this feedback to continuously improve the content.
5. Freshdesk
Freshdesk is a cloud-based customer support software developed by Freshworks. It offers a range of tools to streamline customer conversations across multiple channels. One of its standout features is the AI-powered knowledge base that aids both agents and customers in finding solutions quickly.
Key Features:
- Freddy AI: Freshdesk’s AI engine, Freddy, powers the platform’s automation, analytics, and knowledge base capabilities. It uses machine learning to provide predictive support and instant solutions.
- Solution Suggester: When agents are responding to tickets, Freddy AI suggests relevant knowledge base articles that can help resolve the customer’s issue.
- Smart Article Suggestions: As customers type their queries in the search bar, the AI provides real-time article suggestions that might answer their questions.
- Feedback Mechanism: Customers can rate and provide feedback on articles, helping businesses understand which content is most helpful and which might need improvement.
6. Intercom
Intercom stands out as a conversational platform designed to foster meaningful relationships between businesses and their customers. Beyond just livechat functionalities, Intercom’s strength lies in its AI-driven knowledge base, which acts as a first line of defence in customer support, offering immediate answers and reducing the need for live agent interactions.
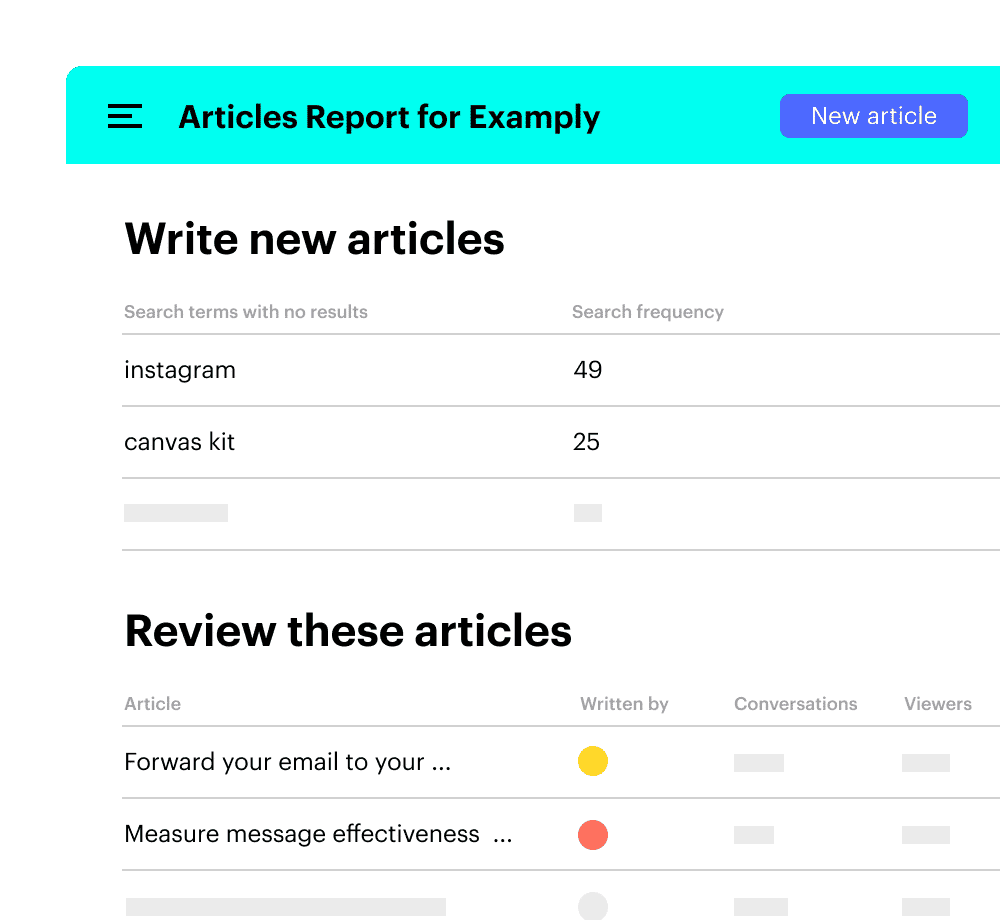
Key Features:
- Resolution Bot: This AI-powered bot instantly addresses customer queries by sourcing answers from the knowledge base, ensuring rapid response times.
- Dynamic Article Suggestions: As queries are typed, Intercom proactively offers relevant knowledge base articles, often preempting and resolving issues before they escalate.
- Feedback Loop: Customers can rate articles, providing invaluable insights into content effectiveness and areas ripe for enhancement.
- Integrated Analytics: Gain a bird’s-eye view of the performance of your knowledge base – from top-performing articles to potential content gaps, ensuring continuous improvement.
Empower Customers to Self-Serve
In conclusion, AI has the potential to significantly enhance traditional knowledge bases in a number of ways. By automating content creation and updating, enhancing content discovery and delivery, and optimizing content quality and performance, AI can make knowledge bases more efficient, effective, and user-friendly.